At the time of this writing, there have been 30 versions of Excel that stretch from 1985 to the current year, running on three different operating systems. Each version might be slightly or significantly different than the last.
If you’re working with Excel, just learning it, or troubleshooting an issue, it’s important to know which version you are using. There are also some tips and tricks to upgrade versions, work between different versions, and deal with compatibility issues.
This piece should clear up any differences between the major releases of Excel, how file compatibility works between versions, and what you can do to upgrade. If you have more questions about Excel, a live chat session with Excelchat can provide the answers.
Learn about the different versions of Excel and how to upgrade your software.
Which Excel Version Do I Have?
Some of the major Excel versions that you’ll probably run across include Excel 2003, 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, and Excel365. But, which version are you currently working with? Depending on your version, here are the actions to take:
- In Excel 2003, go to the Help tab, and click on About Microsoft Excel.
- In Excel 2007, click on the rounded Microsoft icon in the top left corner, and click on Excel options > Resources > About.
- In Excel 2010, click on File > Help > About Microsoft Excel.
- In Excel versions 2013 and 2016, go to File > Account > About Excel.
About the Different Excel Versions
There are too many versions of Excel to list and outline, but here are some of the major releases and what you need to know.
- Excel 2003. This was the first version of Excel to offer tables and the first to have the “WIMP” (Windows, Icons, Menus, Point) interface. It was released for both Windows and Mac operating systems.
- Excel 2007. This release was only provided for Windows and it was the first Excel version to have the Ribbon interface. It also changed the file format from .xls to .xlsm and .xlsx files. This expanded the number of rows that a file could hold to 1 million and improved file security.
- Excel 2010. This version was also only released for Windows. Some of the new features included Ribbon customizations, multi-threading support, and sparklines.
- Excel 2013. This version was only available for Windows and features included Slicers, Flash Fill, and dozens of new functions.
- Excel 2016. This version was released for both Windows and Mac, and it includes regular feature updates released online.
- Excel365. This is a subscription-based version of Excel 2016 that is 100% online and regularly updated. You don’t need to do anything to make this happen.
How to Update Excel
If you have an older version of Excel and want to update it, how you do this will depend on which version you are currently running. Support has ended for Office 2003 and 2007, so it would be a good idea to buy and install the latest version.
If you have Excel 2010, go to File > Help > Check for Updates. If there are updates available, choose Install Updates.
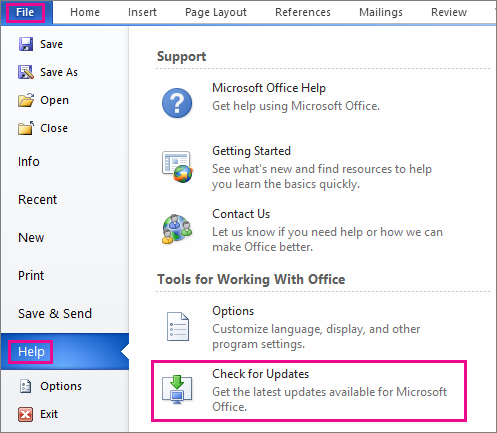
If you have Excel 2013, go to File > Account. Choose Update Options under Product Information. Select Enable Updates. Click Update Now to check for and install any updates.

How to Use Excel Files Created from Earlier Versions of Excel
Once you’ve installed a new version of Excel or upgraded, you might want to know how this is going to impact your existing files. When you have files that were created in an earlier version of Excel, backward compatibility will work in various ways:
- Use compatibility mode. Compatibility Mode allows you to open and work with Excel files that were created in earlier versions than the one you have. However, this isn’t available for Excel 2007 files.
- Download a file converter. You can use a file converter to download and open Excel files in earlier versions of Excel.
Versions 2010 and later of Excel allow you to open files that were created in 97-2003 versions in compatibility mode. This should be automatic. However, any new features that were created in Excel after the file was created will not be available in this mode.
If you don’t want to work on a workbook in compatibility mode, you have the option to convert the file to a format that is consistent with the new version of Excel.
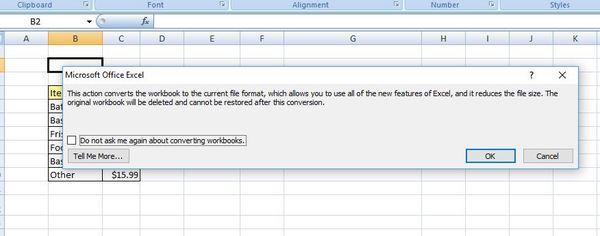
If you have an Excel file that is from Excel 97-2003 and you try to open it in a later version, you might be prompted to “convert” the file. Assuming the file is in .xls format, and you don’t plan to work on it in that format again in the future, you can convert it to an XML format (.xlsx, .xltm, .xlsb, .xltx, .xlsm).
After the conversion, you’ll have access to the new features and functions of your current Excel version. To convert a workbook, take the steps:
- Open the workbook (this will happen in compatibility mode).
- Go to File > Info > Compatibility Mode > Convert.
- Click OK.
If you want to have copies of the old file format and convert to the new file format, simply go to File > Save As. Keep the same file name if you wish but choose a new extension under Save as type. Click Save.

Hopefully, you found the information you were looking for regarding working with different versions of Excel. If you still need to troubleshoot a particular issue, or want one-on-one training in Excel, find out how Excelchat can help.
Our friendly Excel experts are available 24/7 to give you the assistance you need. Just open a live chat window to get started. Your first session is always free.














Leave a Comment